Python QuickStart
Prerequisites
- Python 3.6+: run
python --versionorpython3 --versionin a terminal to check the installed version. - A running SITL instance (jMAVSim, gazebo, …). A quick way to run a headless gazebo SITL instance using docker is documented here.
Install
MAVSDK-Python is distributed through PyPi, and can therefore be installed with pip3:
pip3 install mavsdk
Make sure that the output of this command confirms that the installation succeeded!
On some systems, you may have to run
pip3 install --user mavsdk, or you may want to run in a Python venv.
For the quick start below we will also install the lightweight package called “aioconsole”.
This provides a REPL (interactive shell) called apython that we can use for running asyncio code:
pip3 install aioconsole
Run SITL
It is always good to make sure that SITL works before trying to connect MAVSDK to it.
One way is to run the following commands in the pxh> prompt when SITL is running:
commander takeoff
commander land
The simulated drone should takeoff and land. If it doesn't, it may mean that SITL is not ready, or that there is a problem.
Take off from MAVSDK
When we know that the simulator is ready, we can open an apython REPL:
apython
Import MAVSDK into the environment by entering:
from mavsdk import System
We then create a System object, in this case named drone, and make it connect to the drone (this object is our "handle" to access the rest of the MAVSDK functions):
drone = System()
await drone.connect()
Once connected, we can arm and takeoff using the appropriate MAVSDK commands:
await drone.action.arm()
await drone.action.takeoff()
If everything went well, your drone should takeoff.
In the pxh console, you should see a log line like:
INFO [commander] Takeoff detected
If running a graphical interface, you should see the drone taking off. Here is what it looks like in jMAVSim:

Make sure to send the
takeoff()command within (at most) a few seconds ofarm(); the drone will automatically disarm after a few seconds if it does not receive a command to takeoff.
You get an exception, as shown below:
raise ActionError(result, “arm()”)
mavsdk.generated.action.ActionError: COMMAND_DENIED: ‘Command denied’; origin: arm(); params: ()
This is not a bug! It means that the arm() call was rejected by PX4, with the error code COMMAND_DENIED.
It happens for instance when you try to arm before the drone gets a GPS fix.
Most functions in MAVSDK-Python can raise exceptions that your code should handle with try... except.
Now that the drone is flying, we can land:
await drone.action.land()
We have been using the apython REPL to run all that interactively, but the same can be achieved by running the takeoff_and_land.py example (in which case the
aioconsolepackage is not needed).
Using an IDE
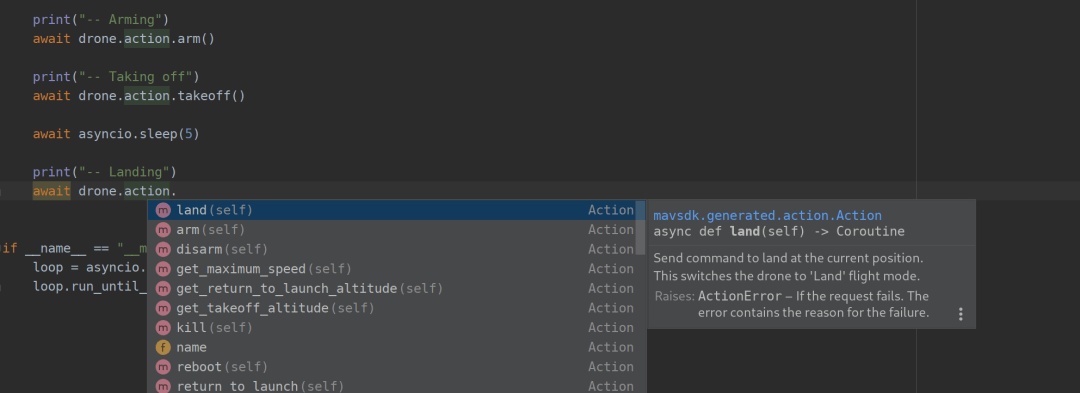
Running from the REPL is convenient for testing a few commands interactively, but aioconsole does not provide auto-completion.
However, IDEs like PyCharm do.
This is very helpful, as typing drone. is enough to get a list of suggestions.
The following screenshot shows PyCharm auto-completion for drone.action.:
Examples
We do have a number of examples available in the repository, which are certainly a good starting point for learning about MAVSDK-Python.
Next Steps
Once MAVSDK is installed we recommend you:
- Try the other examples
- Browse the API reference to get an overview of the functionality.

